With the rapid advancements in technology, online banking has become an integral part of our daily lives. It offers convenience and accessibility, allowing us to manage our finances with just a few clicks. However, these conveniences come with a potential downside – cyber threats and vulnerabilities that can put our financial information at risk.
The emergence of cybercriminals and their sophisticated techniques poses a major challenge for banking institutions. One such risk is phishing, where cybercriminals trick unsuspecting users into revealing their sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords, through deceptive emails or websites. These stolen credentials can then be used to gain unauthorized access to online banking accounts, leading to unauthorized transactions and financial loss.
Another significant vulnerability in online banking is malware. Cybercriminals use malicious software to gain access to users’ devices, allowing them to monitor and intercept online transactions. This can result in the compromise of personal and financial information, as well as the installation of additional malware or ransomware, which can encrypt files or demand a ransom for their release.
Furthermore, online banking systems may be vulnerable to data breaches, where a hacker gains unauthorized access to the banking institution’s network and steals sensitive customer information. This can include personal data, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and financial data, compromising the privacy and security of individuals involved.
To mitigate these risks, both banking institutions and users need to be proactive in implementing robust cybersecurity measures. This includes regularly updating software and security patches, using strong and unique passwords for online accounts, and being vigilant in recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts. Additionally, banks should invest in advanced security technologies, such as multi-factor authentication and encryption, to enhance the protection of customer information.
In conclusion, while online banking offers convenience and flexibility, it also comes with inherent cybersecurity risks. Understanding these vulnerabilities and taking necessary precautions can help safeguard our financial information and ensure a safer online banking experience.
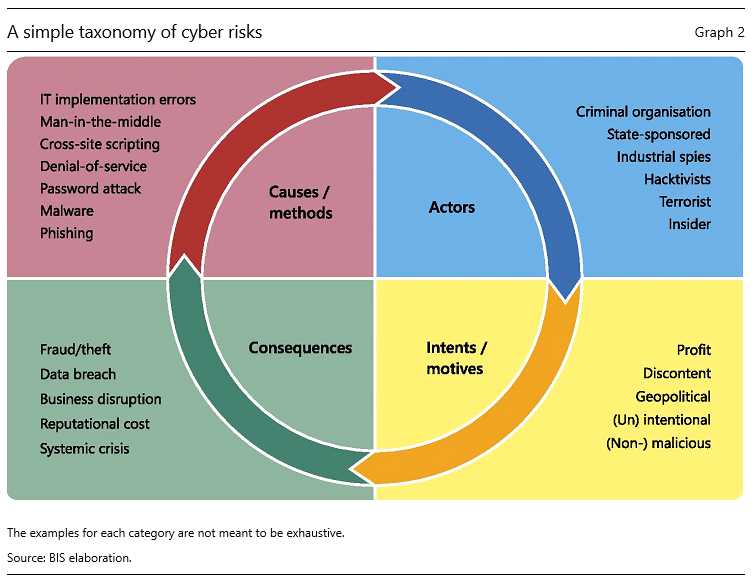
Cybersecurity Risks in DeBank
In today’s digital age, the convenience of online banking has become an integral part of our lives. However, with this convenience comes great cybersecurity risks. DeBank, like any other online banking platform, is not exempt from these risks.
One of the main cybersecurity risks associated with DeBank is phishing attacks. Phishing involves tricking users into providing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and financial details by impersonating a trustworthy entity. Hackers may send fraudulent emails or set up fake websites that mimic the DeBank login portal, luring unsuspecting users into revealing their credentials.
Another significant risk is malware and viruses. Cybercriminals can infect users’ devices with malware or viruses through malicious attachments, downloads, or infected websites. Once infected, these malicious programs can steal personal information, such as login credentials, or even take control of the user’s device.
Weak authentication methods also pose a significant risk to cybersecurity in DeBank. If the platform utilizes weak or easily guessable passwords, cybercriminals can use automated tools to brute force their way into user accounts. Additionally, if multi-factor authentication is not enforced, an attacker who obtains a user’s credentials can easily gain unauthorized access to their account.
Social engineering attacks are another cybersecurity risk in DeBank. Social engineering involves manipulating users into divulging sensitive information by exploiting their trust or emotions. Cybercriminals may pose as DeBank representatives over the phone or through email, convincing users to disclose their credentials or other personal information.
Lastly, DeBank may also face the risk of insider threats. These threats can come from disgruntled employees or contractors with authorized access to the platform’s systems. If these individuals have malicious intentions, they can abuse their privileges to steal sensitive information or sabotage the platform’s operations.
In conclusion, while online banking offers convenience, it also exposes users to various cybersecurity risks. DeBank, like any other online banking platform, must constantly update its security measures to mitigate the risks associated with phishing attacks, malware and viruses, weak authentication methods, social engineering, and insider threats.
Understanding the Weaknesses in Online Banking
As online banking continues to gain popularity and more individuals rely on it for their financial transactions, it becomes crucial to understand the weaknesses inherent in this system. While online banking offers convenience and efficiency, it also exposes users to various cybersecurity risks.
One of the biggest weaknesses in online banking is the susceptibility to phishing attacks. Phishing involves cybercriminals posing as legitimate financial institutions or service providers to trick users into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. These fraudulent emails or websites deceive users into believing they are interacting with a trusted entity, making them more likely to disclose their credentials unknowingly.
Another significant weakness is the potential for malware infections. Cybercriminals design malicious software, such as keyloggers or trojans, to infiltrate users’ systems and steal sensitive information. Malware can be delivered through infected email attachments, fake software updates, or compromised websites. Once installed, it can record keystrokes, capture login credentials, and even gain unauthorized access to banking transactions. This weakness highlights the importance of regularly updating antivirus software and being cautious when interacting with unfamiliar or suspicious online content.
Weak passwords are another vulnerability in online banking. Many users opt for weak passwords that are easy to remember but also easy for hackers to guess. Common mistakes include using personal information, simple dictionary words, or easily guessable sequences of numbers. By creating strong and unique passwords, users can significantly enhance their online banking security. It is also crucial to enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of protection.
Social engineering is another weakness that cybercriminals exploit in online banking. By impersonating bank representatives or customer service agents, scammers trick users into providing confidential information or performing unauthorized transactions. These social engineering tactics play on human trust and often rely on persuasive techniques to deceive victims. It is essential to remain vigilant and verify the identity of individuals requesting sensitive information before providing any details.
Lastly, the vulnerability of public Wi-Fi networks poses a significant risk to online banking security. Public networks are often unsecured and leave users susceptible to interception and data theft. Hackers can easily eavesdrop on network traffic and capture sensitive information transmitted by users. To mitigate this weakness, it is advisable to use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) when accessing online banking services on public networks. VPNs encrypt internet traffic, ensuring a secure connection between the user’s device and the online banking platform.
Understanding these weaknesses helps users make informed decisions and take appropriate measures to protect their online banking transactions. By staying aware of these vulnerabilities and adopting best security practices, individuals can reduce the likelihood of falling victim to cyberattacks and ensure a safer online banking experience.
A Brief Overview of Online Banking
Online banking, also known as internet banking, is a convenient and increasingly popular way for individuals to manage their finances. With the rise of technology, banking institutions have shifted to offering online services to cater to the demands of their customers. Online banking provides users with the ability to perform various financial transactions and access banking services remotely through the internet.
There are several advantages to online banking. One of the main benefits is the convenience it offers. Unlike traditional banking, online banking allows users to access their accounts and perform transactions at any time and from anywhere with an internet connection. This eliminates the need to visit a physical bank branch, saving time and effort. Additionally, online banking offers a wide range of services, including checking account balances, transferring funds between accounts, paying bills, and even applying for loans.
Another advantage of online banking is enhanced security. Banking institutions implement advanced security measures to protect customer data and ensure the integrity of online transactions. These measures may include encryption, two-factor authentication, and fraud detection systems. However, it is important for users to be vigilant and follow cybersecurity best practices to prevent unauthorized access to their accounts.
Despite the numerous benefits, online banking also comes with certain risks. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in online banking systems. Phishing attacks, malware, and identity theft are some of the common cybersecurity risks faced by online banking users. It is crucial for individuals to stay informed about the latest threats and take appropriate measures to safeguard their personal and financial information.
In conclusion, online banking is a convenient and efficient way for individuals to manage their finances. It offers multiple benefits, including convenience, accessibility, and enhanced security. However, it is important for users to remain cautious and implement necessary security measures to protect themselves from cyber threats. For more information on online banking and its risks, visit price today debank.
The Importance of Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity plays a vital role in today’s digital world as we rely heavily on technology for various aspects of our lives. With the increasing use of online banking services, it is imperative to understand the importance of cybersecurity to protect our financial information.
One of the key reasons why cybersecurity is crucial is because it helps to safeguard our personal and financial data from unauthorized access. Online banking platforms store a vast amount of sensitive information, such as account numbers, passwords, and social security numbers. Without proper cybersecurity measures in place, this data can be easily compromised, leading to identity theft, fraud, and financial loss.
Cybersecurity also helps to maintain the trust and confidence of customers in online banking services. When customers feel that their personal information is secure, they are more likely to engage in online transactions and take advantage of the convenience offered by online banking. On the other hand, a breach in cybersecurity can shake customer confidence, resulting in a decline in the usage of online banking services.
Furthermore, cybersecurity is essential for protecting the integrity and stability of financial institutions. Cyber attacks not only target individual customers but also aim to disrupt the operations of banks and financial systems as a whole. A successful cyber attack on a financial institution can have far-reaching consequences, leading to loss of funds, disruption of services, and damage to the reputation of the institution.
Lastly, cybersecurity is crucial for the overall stability of the economy. As online banking becomes increasingly prevalent, the interconnectedness of financial systems and institutions creates a ripple effect. A breach in cybersecurity can propagate across the financial industry, leading to widespread economic repercussions. Therefore, strong cybersecurity practices are necessary to maintain the stability and resilience of the economy.
In conclusion, cybersecurity is of utmost importance in online banking due to the sensitive nature of financial information, the need to maintain customer trust, the protection of financial institutions, and the overall stability of the economy. By prioritizing cybersecurity measures, both individuals and institutions can mitigate the risks associated with online banking and ensure the continued growth of digital financial services.
Common Cybersecurity Risks

Online banking has become an integral part of our lives, providing convenience and ease of access to our financial accounts. However, it also comes with its fair share of cybersecurity risks. Understanding these risks is crucial for users to protect themselves and their finances. Here are some of the common cybersecurity risks associated with online banking:
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing is a common tactic used by cybercriminals to trick users into revealing their sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. These attacks often involve sending deceptive emails or creating fake websites that appear to be legitimate banking platforms.
- Malware Infections: Malware, such as viruses, worms, and trojans, can infect users’ devices and compromise their online banking security. These malicious programs are usually spread through infected email attachments, compromised websites, or downloaded software.
- Weak Passwords: Many users still use weak passwords that are easy to guess or crack. Attackers can exploit this weakness and gain unauthorized access to users’ online banking accounts. It is important to use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks, especially those without passwords, pose a significant cybersecurity risk. Attackers can intercept sensitive information transmitted over these networks, compromising users’ online banking security. It is advisable to use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) or a trusted mobile network when accessing online banking services.
- Outdated Software: Using outdated operating systems, browsers, and software increases the risk of cyberattacks. Hackers often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access or infect users’ devices with malware. Regularly updating software and using security patches is essential to minimize these risks.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineering involves manipulating users into revealing their confidential information. Cybercriminals may impersonate bank representatives or use psychological tactics to deceive users. It is important to be cautious and verify the authenticity of any communication regarding online banking.
By being aware of these common cybersecurity risks and adopting the necessary protective measures, users can greatly enhance their online banking security and safeguard their finances.
Phishing Attacks
One of the most common cybersecurity risks in online banking is phishing attacks. Phishing attacks are fraudulent attempts to deceive individuals into disclosing their personal and sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details.
In a typical phishing attack, cybercriminals send fraudulent emails or messages that appear to be from a legitimate financial institution, such as DeBank. These emails often contain convincing logos, branding, and language to trick recipients into believing they are interacting with a trusted source.
The phishing emails usually encourage recipients to click on a link that leads to a malicious website designed to resemble the legitimate DeBank website. Once on the fake website, users are prompted to enter their login credentials or other sensitive information.
Once the cybercriminals obtain the users’ information, they can use it to gain unauthorized access to their accounts, perform fraudulent transactions, or even steal their identity.
Phishing attacks can also be carried out through other channels, such as phone calls or text messages, commonly known as voice phishing (vishing) and SMS phishing (smishing) respectively. These methods aim to manipulate individuals into providing their personal information over the phone or by responding to fraudulent messages.
To minimize the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks, DeBank and its customers should be aware of the following precautions:
| 1. Verify the email sender: | Always double-check the email address of the sender. Legitimate emails from DeBank will come from an official domain (e.g., debank.com) and not from suspicious or unknown email addresses. |
| 2. Avoid clicking on suspicious links: | Hover over links in emails to see the actual website address they lead to. If the URL looks suspicious or different from DeBank’s official website, do not click on it. |
| 3. Be cautious of urgency or threats: | Phishing emails often create a sense of urgency or use threats to pressure individuals into taking immediate action. Be suspicious of emails that demand urgent account updates or threaten account suspension. |
| 4. Enable two-factor authentication: | Implementing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of verification, such as a code sent to their mobile device, in addition to their password. |
| 5. Educate employees and customers: | DeBank should regularly educate its employees and customers about phishing attacks, their characteristics, and how to identify and report potential phishing attempts. |
By implementing these precautions, DeBank can significantly reduce the risks associated with phishing attacks and protect its customers’ sensitive information.
Malware and Ransomware
Malware and ransomware are two common and significant cybersecurity risks that can greatly impact the security and stability of online banking systems like DeBank. Malware, short for malicious software, is a term used to describe a variety of software programs that are designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems. Ransomware, on the other hand, is a type of malware that specifically aims to encrypt files or data on a victim’s computer and then demands a ransom in return for the decryption key.
Malware can infect a user’s computer or mobile device through various means, such as email attachments, malicious websites, or compromised software installations. Once installed, malware can have damaging effects, such as stealing sensitive information (such as login credentials or financial data), disrupting system operations, or even taking control of the entire system. In the context of online banking, this can lead to unauthorized access to user accounts, financial fraud, and identity theft.
Ransomware, on the other hand, poses a different type of threat to online banking systems. Once a user’s device is infected with ransomware, the malware essentially holds the user’s files or data hostage by encrypting them and making them inaccessible. The attackers then demand a ransom, typically in the form of cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key. If the user refuses to pay the ransom, the attackers may threaten to permanently delete the encrypted files or publicly release the compromised data, causing irreparable damage to the user.
Impact of Malware and Ransomware on Online Banking
The impact of malware and ransomware attacks on online banking can be severe. Not only can these attacks result in financial losses for both banks and customers, but they can also erode trust in the online banking system as a whole. Customers may lose confidence in the security of their accounts and be reluctant to engage in online banking activities, leading to a decrease in customer satisfaction and adoption rates.
Furthermore, successful malware or ransomware attacks can also result in legal and regulatory consequences. Banks and financial institutions are required to comply with various security and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in the United States. A data breach caused by malware or ransomware can lead to substantial penalties and reputational damage.
Preventative Measures and Best Practices
Preventing malware and ransomware attacks requires a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. Some key preventative measures and best practices include:
| 1. Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-malware software |
| 2. Regularly backup important files and data |
| 3. Be cautious when opening email attachments or clicking on suspicious links |
| 4. Keep software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches |
| 5. Enable two-factor authentication for online banking accounts |
| 6. Educate users about phishing attacks and other common malware delivery methods |
By implementing these preventative measures and best practices, banks and online banking users can significantly reduce the risk of malware and ransomware attacks. It is essential for individuals and organizations alike to stay vigilant and proactive in protecting their systems and data from these evolving cybersecurity threats.
Social Engineering Threats
Social engineering is a tactic often used by cybercriminals to manipulate individuals into providing sensitive information or performing actions that can compromise the security of online banking systems. By exploiting human emotion and trust, social engineering attacks aim to deceive and manipulate bank customers or employees.
Phishing

Phishing is a common social engineering attack method where cybercriminals send fake emails, text messages, or make phone calls posing as legitimate institutions, such as banks, to trick individuals into revealing their login credentials, personal information, or initiating unauthorized transactions.
These phishing messages often imitate the look and feel of legitimate communication from the bank, making it difficult for users to identify the fraudulent nature of the request. It’s important for bank customers to be cautious and verify the authenticity of any communication before sharing any sensitive information.
Pretexting
Pretexting involves creating a false scenario or pretext to deceive individuals into disclosing confidential information. This can include pretending to be a bank representative, security personnel, or someone with authority who needs access to personal information or account details.
The cybercriminal may use various believable tactics, such as gaining the victim’s trust through engaging conversations, offering assistance or rewards, or threatening with consequences if the requested information is not provided. It is crucial for individuals to be skeptical and verify the identity of anyone requesting sensitive information.
Baiting
Baiting is a social engineering technique where cybercriminals entice individuals with a promise of a reward or benefit to manipulate them into taking an action that could compromise their online banking security. This can include downloading malicious software, visiting compromised websites, or disclosing personal information.
Common baits can be in the form of free software downloads, special offers, or enticing links or advertisements. It is important for bank customers to exercise caution when encountering such offers and to refrain from clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown software.
Social engineering threats pose a significant risk to online banking systems and require individuals to stay vigilant, question requests for sensitive information, and report any suspicious activities or communications to their bank. By raising awareness and adopting security best practices, customers can better protect themselves and their financial information from these threats.
Weak Passwords
One of the major cybersecurity risks in the DeBank online banking system is the use of weak passwords by users. A weak password consists of easily guessable or common words, such as “123456” or “password”.
Weak passwords are a significant vulnerability because they can be easily exploited by cybercriminals using various techniques, such as brute-force attacks or dictionary attacks. These attacks involve systematically trying different combinations of characters or words until the correct password is found.
To mitigate this risk, it is crucial for users to create strong and unique passwords for their DeBank online accounts. A strong password should:
1. Be Long
A longer password is generally more secure as it increases the number of possible combinations that an attacker would need to try. Ideally, a password should be at least 12 characters long.
2. Include a Combination of Characters
A strong password should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. This complexity further increases the difficulty of guessing or cracking the password.
It is also important for users to avoid using easily guessable information, such as their name, birthdate, or common words, as part of their password. Additionally, reusing passwords across multiple online accounts should be avoided, as it increases the risk of a compromised password being used to gain unauthorized access to other accounts.
Conclusion:
By creating and maintaining strong passwords, DeBank users can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to their online banking accounts. It is essential to regularly update passwords and enable multi-factor authentication for an added layer of security.
Unsecure Networks
One of the major cybersecurity risks that individuals and organizations face when using online banking services is the use of unsecure networks. Unsecure networks refer to any network that lacks the necessary security measures to protect sensitive data transmitted over it.
What are Unsecure Networks?
Unsecure networks are networks that do not have proper encryption protocols or security measures in place. These networks can include public Wi-Fi networks, as well as poorly secured home or office networks.
When connected to an unsecure network, the data transmitted between the user and the online banking service can easily be intercepted by hackers or malicious actors. This puts users at risk of having their login credentials, account details, and other sensitive information stolen.
The Risks of Using Unsecure Networks for Online Banking
The use of unsecure networks poses several risks for online banking users:
| Risk | Description |
| Data interception | Hackers can intercept and read the data transmitted over an unsecure network, potentially gaining access to login credentials, account numbers, and other sensitive information. |
| Man-in-the-middle attacks | Attackers can position themselves between the user and the online banking service, intercepting and manipulating the communication to redirect funds or gather sensitive information. |
| Phishing attacks | Cybercriminals can set up fake networks that mimic legitimate ones, tricking users into connecting to them and capturing their login credentials and personal information. |
To mitigate the risks associated with unsecure networks, it is important for online banking users to always connect to secure networks, such as their home or office networks, or use trusted and encrypted virtual private networks (VPNs) when accessing online banking services on public Wi-Fi networks.
By taking precautions and being aware of the risks, users can help protect themselves and their financial information from cyber threats when using online banking services.
Data Breaches
Data breaches pose a significant risk to online banking systems, exposing customer data to unauthorized access and potential misuse. These breaches occur when cybercriminals successfully breach the security measures put in place by banks and gain access to sensitive customer information.
During a data breach, personal and financial information, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and banking details, can be compromised. This information can then be used for various malicious purposes, including identity theft, fraud, and unauthorized financial transactions.
One common method used by cybercriminals to carry out data breaches is through hacking. They exploit vulnerabilities in the bank’s network infrastructure, systems, or applications to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Additionally, phishing attacks, malware, and social engineering techniques are commonly employed to trick customers into revealing their login credentials or other sensitive information.
Once cybercriminals gain access to customer data, they can sell it on the dark web or use it themselves to commit fraud. They may impersonate customers, open unauthorized accounts, or make unauthorized purchases using stolen financial information. The consequences of data breaches can be severe, leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and a loss of trust from customers.
Financial institutions must implement robust security measures to protect customer data and mitigate the risk of data breaches. This includes regular security audits, encryption of sensitive data, implementing multi-factor authentication, and educating customers about cybersecurity best practices. Additionally, banks should have incident response plans in place to minimize the impact of a data breach and aid in the recovery process.
Ultimately, the threat of data breaches underscores the importance of cybersecurity in the online banking sector. By investing in robust security measures and educating both employees and customers about cyber threats, banks can reduce the risk of data breaches and safeguard their customers’ sensitive information.
Insider Threats
One of the most significant cybersecurity risks faced by online banking platforms like DeBank is the threat of insider attacks. Insider threats occur when individuals with authorized access to sensitive information and systems misuse their privileges or intentionally cause harm to the organization.
Insiders can include employees, contractors, or even trusted third-party service providers. These individuals have a deeper understanding of the organization’s infrastructure and security protocols, making it easier for them to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access.
There are several types of insider threats that can impact online banking platforms:
- Malicious Insiders: These are individuals who intentionally cause harm to the organization, whether it is for personal gain, revenge, or ideological reasons. They may engage in activities like stealing customer data, manipulating transactions, or even sabotaging the system.
- Negligent Insiders: Negligent insiders pose a significant risk to online banking platforms as they are not intentionally malicious but can cause harm through their carelessness. This includes actions like failing to follow security protocols, sharing sensitive information with unauthorized individuals, or falling victim to phishing attacks.
- Compromised Insiders: In some cases, insiders may unintentionally become compromised by external actors. This can include individuals who fall victim to social engineering attacks or unknowingly install malware on their devices, providing cybercriminals with access to sensitive systems and information.
Addressing insider threats requires a multi-pronged approach. Banks and other financial institutions must implement strict access controls and monitoring systems to detect any suspicious activity. Regular training and awareness programs should be conducted to educate employees about the risks and consequences of insider threats.
Additionally, organizations should implement employee satisfaction and support programs to address any internal issues promptly. By creating a positive work environment and promoting transparency, organizations can help reduce the likelihood of insider attacks.
Overall, insider threats pose a significant challenge to the cybersecurity of online banking platforms. By understanding the different types of insider threats and implementing appropriate measures to mitigate these risks, organizations can better protect their systems, sensitive information, and their customers from harm.
Third-party Vendor Risks

As online banking continues to evolve, many financial institutions are relying on third-party vendors to provide essential services and support. While outsourcing certain functions can offer benefits such as cost savings and specialized expertise, it also introduces a new set of cybersecurity risks.
Third-party vendors often have access to sensitive customer data and play a critical role in the operations of a bank. However, their security measures may not be on par with those of the bank itself. This creates a potential weak link in the cybersecurity chain, as cybercriminals may target the vendors and exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to the bank’s systems.
Key risks associated with third-party vendors include:
Data breaches: If a third-party vendor experiences a data breach, it could lead to the exposure of confidential customer information. This puts both the bank and its customers at risk of identity theft, financial fraud, and other cybercrimes.
Inadequate security practices: Third-party vendors may not have the same level of cybersecurity expertise or resources as a financial institution. This could result in inadequate security measures, such as weak passwords, outdated software, or insufficient encryption protocols, which can be exploited by cyber attackers.
Supply chain attacks: Cybercriminals may target a third-party vendor to gain access to the bank’s systems. By compromising a vendor’s network or software, attackers can bypass the bank’s security defenses and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or launch further attacks.
Lack of visibility and control: Relying on third-party vendors means relinquishing some level of visibility and control over cybersecurity practices. Banks may not have full insight into how their vendors secure customer data, making it challenging to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and internal security standards.
To mitigate these risks, financial institutions must carefully vet and monitor their third-party vendors. This includes conducting thorough due diligence, assessing their security controls and protocols, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, banks should establish clear contractual agreements that outline security expectations and responsibilities.
In conclusion, while third-party vendors can bring valuable services to online banking, they also introduce new cybersecurity risks. Financial institutions must take steps to manage these risks effectively and ensure the security of customer data and systems.
Mobile Banking Vulnerabilities

Mobile banking has become increasingly popular due to its convenience and accessibility. However, this rise in usage also introduces new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial in order to protect ourselves and our financial information.
1. Device Theft or Loss
One of the greatest risks of mobile banking is the potential loss or theft of your device. If your smartphone or tablet falls into the wrong hands, your personal and financial information could be compromised. It is important to secure your device with a strong passcode or biometric authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Malware and Phishing Attacks
Mobile devices are also susceptible to malware and phishing attacks. Cybercriminals can trick users into downloading malicious apps or clicking on phishing links that mimic legitimate banking websites. These attacks can lead to the theft of login credentials, personal data, and even money from your bank account. It is crucial to only download apps from trusted sources and to be cautious of suspicious links or emails.
| Vulnerability | Description | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Device Theft or Loss | Potential loss or theft of your mobile device. | – Secure your device with a strong passcode or biometric authentication. – Enable remote tracking and wiping capabilities. – Regularly backup your data. |
| Malware and Phishing Attacks | Cybercriminals trick users into downloading malicious apps or clicking on phishing links. | – Only download apps from trusted sources. – Be cautious of suspicious links or emails. – Keep your operating system and apps updated. – Install reputable security software. |
| Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks | Using unsecured Wi-Fi networks can expose your mobile device to data interception. | – Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for mobile banking. – Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for secure internet connection. – Enable two-factor authentication for extra security. |
3. Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks
Using unsecured Wi-Fi networks can expose your mobile device to data interception. Cybercriminals can intercept the data transmitted between your device and the banking server, potentially gaining access to your sensitive information. To protect against this vulnerability, it is recommended to avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for mobile banking. Instead, use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to establish a secure internet connection. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step for logging into your mobile banking account.
By understanding and addressing these mobile banking vulnerabilities, you can better protect yourself from cyber threats and enjoy the convenience of banking on the go.
Emerging Threats in Online Banking
As online banking continues to grow in popularity, it is also becoming an increasingly attractive target for cybercriminals. New threats are constantly emerging, and it is vital for both banks and customers to stay aware and prepared.
1. Account Takeover: Hackers are constantly finding new ways to gain unauthorized access to online banking accounts. This can include stealing login credentials through phishing emails or using malware to capture keystrokes. Once they have access, hackers can steal funds, make unauthorized transactions, or gain access to sensitive personal information.
2. Mobile Banking Vulnerabilities: With the rise of mobile banking apps, there are new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals are exploiting. Malicious apps, fake banking apps, and insecure Wi-Fi networks can all put mobile banking users at risk. These threats can lead to the theft of personal and financial information or even the installation of malware on the mobile device.
3. Social Engineering: Cybercriminals are increasingly using social engineering techniques to manipulate users into revealing sensitive information. This can include impersonating bank personnel, sending fake emails or text messages, or creating fake websites. By tricking customers into divulging their login credentials or other personal information, cybercriminals can gain access to their online banking accounts.
4. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are sophisticated cyber attacks that are often targeting financial institutions. These attacks are typically carried out by well-funded and highly skilled hacker groups. APTs can be difficult to detect and can cause significant damage, such as stealing customer data, disrupting banking operations, or even manipulating financial markets.
5. Insider Threats: Employees or contractors within a bank can pose a significant risk to online banking security. Whether through intentional actions or accidental mistakes, insiders can leak sensitive information, install malware, or compromise the security of the bank’s IT infrastructure. Implementing strict security protocols and regularly monitoring employee activities are crucial in mitigating insider threats.
6. Internet of Things (IoT) Risks: The growing number of IoT devices connected to the internet opens up new avenues of attack. Devices like smartwatches, home assistants, or smart speakers can be targeted by cybercriminals to gather personal information or gain access to online banking credentials. Banks need to ensure that their online banking platforms are secure against these emerging IoT risks.
As the online banking landscape evolves, so do the threats that come with it. It is essential for banks to invest in robust cybersecurity measures and for customers to stay vigilant and educated about the emerging threats in online banking.
FAQ:,
What are the common cybersecurity risks in online banking?
Common cybersecurity risks in online banking include phishing attacks, malware infections, data breaches, and password theft. These risks can result in financial loss, identity theft, and unauthorized access to personal information.
How can I protect myself from cybersecurity risks in online banking?
To protect yourself from cybersecurity risks in online banking, it is important to keep your devices and software up to date, use strong, unique passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, be cautious of phishing emails and suspicious links, and regularly monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity. It is also a good practice to use secure and trusted banking apps or websites and avoid accessing your accounts from public Wi-Fi networks.
What are some examples of cyber attacks targeting online banking?
Some examples of cyber attacks targeting online banking include phishing emails that trick users into revealing their login credentials, malware infections that steal banking information, ransomware attacks that lock users out of their accounts until a ransom is paid, and man-in-the-middle attacks that intercept and alter communication between users and their banking websites or apps. These attacks can lead to financial loss, identity theft, and unauthorized access to personal information.