
As digital banking becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives, it is essential to take a closer look at its potential weak points and vulnerabilities. While digital banking offers convenience and accessibility, it also exposes users to various risks and threats.
One of the main weak points in digital banking is security. With the rise of cybercrime, hackers are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to sensitive information. This includes personal data, financial details, and login credentials. The consequences of such breaches can be devastating for individuals and businesses alike.
Another weak point in digital banking is the risk of fraud. Cybercriminals are skilled at impersonating legitimate financial institutions and tricking users into sharing their personal information or making unauthorized transactions. This can lead to financial losses for unsuspecting individuals and erode trust in digital banking platforms.
Furthermore, the reliance on technology introduces another vulnerability in digital banking. System glitches, hardware failures, or technological errors can disrupt banking services and hinder customers’ access to their accounts. These technical issues can cause inconvenience and frustration for users, making digital banking less reliable compared to traditional banking methods.
In conclusion, as we embrace the convenience of digital banking, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the weak points that come with it. By implementing robust security measures, educating users about fraud prevention, and ensuring reliable technology infrastructure, we can mitigate the vulnerabilities and make digital banking safer and more reliable for all.
Weak Points in DeBank
As digital banking continues to grow in popularity, it is important to assess its vulnerabilities to protect the financial information of users. DeBank, like any other digital banking platform, has weak points that could be targeted by cybercriminals. By understanding these weaknesses, we can work towards strengthening the security measures in place and ensure the safety of our financial transactions.
| Weak Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | DeBank is susceptible to phishing attacks where users may be tricked into providing their login credentials or personal information on fraudulent websites or through deceptive emails. |
| Weak Passwords | Users who choose weak or easily guessable passwords put their accounts at risk of unauthorized access. DeBank should implement password complexity requirements and encourage users to choose strong passwords. |
| Malware and Viruses | Malicious software or viruses can compromise the security of DeBank and its users. It is essential for the platform to have robust antivirus and anti-malware mechanisms in place to prevent such attacks. |
| Insider Threats | DeBank employees or contractors with access to sensitive user data can pose a significant risk if they misuse or abuse their privileges. Stringent access controls and monitoring should be implemented to mitigate this threat. |
| Network Vulnerabilities | DeBank relies on networks for communication, and any vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure could be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access or intercept sensitive data. Regular network vulnerability assessments and security updates should be carried out. |
It is crucial for DeBank to address these weak points and continuously update their security measures to stay ahead of cyber threats. By doing so, they can build trust with their users and ensure the protection of their financial information.
Security Risks in Digital Banking

Digital banking has revolutionized the way people manage their finances, offering convenience and accessibility like never before. However, with these benefits come inherent security risks that must be addressed to ensure the safety of customer data and financial transactions. In this section, we will discuss some of the key security risks in digital banking.
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a common security risk in digital banking, where cybercriminals impersonate legitimate financial institutions in an attempt to trick customers into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or credit card details. These attacks often come in the form of fake emails, text messages, or phone calls, and can be difficult to spot.
2. Malware and Viruses
Malware and viruses pose a significant threat to the security of digital banking systems. Cybercriminals can use these malicious software programs to gain unauthorized access to customer accounts, steal personal information, or manipulate financial transactions. It is crucial for digital banks to have robust security measures in place to detect and prevent malware and virus attacks.
3. Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access to customer accounts is another security risk in digital banking. Weak passwords, unsecured Wi-Fi networks, or compromised devices can make it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access to online banking platforms. It is important for customers to use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication to protect against unauthorized access.
4. Data Breaches
Data breaches are a major concern for digital banks, as they can result in the exposure of sensitive customer information, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and financial data. Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in the bank’s security infrastructure or target employees with phishing attacks to gain unauthorized access to customer data. Digital banks must prioritize data security and regularly update their systems to protect against data breaches.
5. Social Engineering
Social engineering is a manipulation tactic used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that may compromise their security. In the context of digital banking, social engineering attacks can involve tricking customers into providing their login credentials or transferring funds to fraudulent accounts. It is important for customers to stay vigilant and be skeptical of unsolicited communications or requests for personal information.
In conclusion, while digital banking offers numerous benefits, it also presents security risks that must be addressed. By implementing robust security measures, educating customers about potential risks, and staying proactive in detecting and preventing security breaches, digital banks can ensure the safety and trust of their customers.
Vulnerabilities in DeBank’s Authentication System
DeBank, a prominent digital banking service provided by Project debank, boasts a range of innovative features that offer convenience and flexibility to its users. However, as with any digital platform, it is susceptible to vulnerabilities, particularly in its authentication system.
One of the weaknesses lies in the reliance on weak passwords. Many users tend to choose easily guessable passwords or reuse passwords across multiple platforms. This practice allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to their accounts, potentially leading to financial loss or identity theft.
Another vulnerability is the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA). DeBank currently relies solely on password-based authentication, which can be compromised through various methods like phishing or password cracking. Implementing MFA, such as using SMS verification codes or biometric authentication, would provide an additional layer of security.
Additionally, DeBank’s authentication system may also be vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Without proper rate limiting or account lockout mechanisms, attackers can repeatedly attempt to guess passwords until they find the correct one. Implementing measures like CAPTCHA or temporary lockouts after a certain number of failed login attempts can mitigate this risk.
Furthermore, DeBank should ensure the secure transmission of authentication data. By using encryption protocols like HTTPS, the risk of eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks can be minimized.
In conclusion, while DeBank offers a user-friendly digital banking experience, it is crucial for the company to address these vulnerabilities in its authentication system. By implementing stronger password policies, introducing MFA, protecting against brute-force attacks, and ensuring secure transmission of authentication data, DeBank can enhance the security and trustworthiness of its platform.
Potential Weaknesses in DeBank’s Data Encryption
Data encryption plays a crucial role in securing sensitive information in digital banking systems like DeBank. However, even the strongest encryption methods can have potential weaknesses that cybercriminals could exploit. It is important to identify and address these weaknesses to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of customer data.
One potential weakness is the use of outdated or vulnerable encryption algorithms. As technology advances, encryption algorithms need to be updated to keep up with evolving security threats. If DeBank is using outdated algorithms, it could be susceptible to attacks that exploit known vulnerabilities. Regularly reviewing and updating encryption algorithms is essential to maintain a high level of security.
Another potential weakness is the improper implementation of encryption protocols. Encryption is not just about using strong algorithms, but also correctly implementing them. Weaknesses can arise if encryption keys are not generated securely, if encryption is not applied to all sensitive data, or if there are flaws in the encryption process. A thorough assessment of DeBank’s encryption implementation is necessary to identify and rectify potential weaknesses.
Furthermore, encryption keys are a critical component of data encryption. If encryption keys are weak or easily guessable, it could render the entire encryption process useless. Additionally, if keys are not securely stored and managed, they could be compromised, allowing unauthorized access to encrypted data. Proper key management practices, such as regular key rotation and secure storage, must be implemented to minimize the risk of key-related weaknesses.
Social engineering attacks also pose a threat to data encryption. Cybercriminals may attempt to manipulate individuals within DeBank to disclose encryption keys or bypass encryption measures. Educating employees about common social engineering techniques and implementing strict verification processes can help mitigate the risk of such attacks.
Lastly, the physical security of DeBank’s infrastructure should not be overlooked. While data encryption protects information during transmission and storage, physical security is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to encryption keys and systems. Implementing measures such as secure data centers, restricted access to servers, and surveillance systems can enhance overall security.
In conclusion, while data encryption is essential for digital banking security, it is important to acknowledge and address the potential weaknesses that can undermine its effectiveness. Regular updates to encryption algorithms, proper implementation of encryption protocols, strong key management practices, awareness of social engineering attacks, and robust physical security measures are all necessary to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of customer data in DeBank’s digital banking system.
Examining DeBank’s Mobile Banking Platform
As digital banking continues to grow in popularity, it is important to closely examine the mobile banking platform offered by DeBank. The mobile banking platform plays a crucial role in providing convenient and secure access to banking services for customers. However, it is not immune to vulnerabilities and should be thoroughly examined to ensure the safety of users’ financial information.
One potential weakness of DeBank’s mobile banking platform is the risk of unauthorized access. If a customer’s mobile device is lost or stolen, an unauthorized individual could gain access to their banking information. To mitigate this risk, DeBank should implement strong authentication measures, such as two-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the mobile banking platform.
Another vulnerability to consider is the potential for phishing attacks. Cybercriminals may attempt to trick users into revealing their login credentials or personal information through deceptive emails or text messages. DeBank should educate its customers about these threats and regularly update its security measures to detect and prevent phishing attacks.
Additionally, the mobile banking platform may be susceptible to malware and other malicious software. Customers might unknowingly download malicious apps or visit compromised websites, exposing their sensitive information to cybercriminals. DeBank should implement robust security measures, such as malware detection and encryption, to protect the mobile banking platform from these threats.
Furthermore, DeBank’s mobile banking platform should prioritize regular software updates. Outdated software may contain known vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. By keeping the platform up-to-date, DeBank can protect its customers’ financial data and ensure a secure banking experience.
In conclusion, examining DeBank’s mobile banking platform is essential to identify and address any weaknesses or vulnerabilities. By implementing strong authentication measures, educating customers about phishing attacks, and prioritizing security updates, DeBank can enhance the security and reliability of its mobile banking platform.
The Risks of Phishing Attacks in DeBank
While digital banking offers convenience and ease of use, it also exposes customers to various risks, one of them being phishing attacks. Phishing attacks involve fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card details, or personal information, by disguising as a trustworthy entity.
Phishing attacks in DeBank pose significant risks to customers, as they can result in financial loss, identity theft, and unauthorized access to accounts. Here are some reasons why phishing attacks are particularly dangerous in the context of DeBank:
- User Trust: Phishing attacks often exploit the trust customers have in DeBank’s reputation. Emails or messages that appear to be sent by the bank can trick customers into revealing their credentials or clicking on malicious links.
- Sophistication: Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, making it difficult for customers to identify fraudulent attempts. Attackers use techniques such as email spoofing, creating convincing login pages, or even using voice or SMS messages to deceive customers.
- Financial Loss: If successful, phishing attacks can lead to financial loss for customers. Attackers can gain unauthorized access to accounts and conduct fraudulent transactions, potentially draining funds or making unauthorized purchases.
- Identity Theft: Phishing attacks can also result in identity theft, as attackers can gather personal information from victims. This information can then be used to open fraudulent accounts, apply for loans, or commit other forms of financial fraud.
- Reputation Damage: Phishing attacks targeting DeBank customers can tarnish the bank’s reputation. If customers fall victim to phishing attempts and suffer financial loss or identity theft, they may lose trust in the bank’s security measures, leading to a loss of customers and a damaged brand image.
To mitigate the risks of phishing attacks, DeBank should invest in robust security measures such as multi-factor authentication, employee training to identify phishing attempts, and implementing email filters to detect and block phishing emails. Regular customer education and awareness campaigns are also essential in ensuring customers are informed and vigilant about the risks of phishing attacks.
In conclusion, phishing attacks pose significant risks to both customers and DeBank. By recognizing the dangers posed by phishing attacks and implementing effective security measures, DeBank can protect its customers and maintain their trust in the digital banking services.
Weaknesses in DeBank’s Account Recovery Process
DeBank’s account recovery process is a critical aspect of its overall security framework. It allows customers to regain access to their accounts if they have forgotten their passwords or if their accounts have been compromised. However, this process also has several weaknesses that can make it vulnerable to unauthorized access or fraud.
| Weakness | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient identity verification | DeBank’s account recovery process relies heavily on knowledge-based authentication, such as asking security questions or requesting personal information. However, this method can be easily bypassed if an attacker has access to the customer’s personal information through data breaches or social engineering. | Unauthorized parties may be able to gain access to customer accounts, leading to potential financial loss or identity theft. |
| Weak password reset mechanism | The password reset mechanism used by DeBank may not have adequate security measures in place. For example, the use of easily guessable password reset links or the absence of multi-factor authentication can make it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts. | Attackers may be able to reset passwords and gain control of customer accounts, potentially leading to unauthorized transactions or theft of sensitive information. |
| Limited verification options | DeBank’s account recovery process may only offer limited options for identity verification, such as relying solely on email or SMS verification codes. This can be problematic as attackers can compromise these communication channels or impersonate customers to gain access to their accounts. | Attackers may be able to intercept verification codes or gain control of the customer’s email or phone number, allowing them to take over the account and perform unauthorized actions. |
| Insufficient monitoring and notification | DeBank may not have robust monitoring systems in place to detect suspicious account recovery activities. Additionally, there may be a lack of timely notifications sent to customers when account recovery processes are initiated, making it difficult for them to respond in a timely manner. | Customers may not be aware of unauthorized account recovery attempts or may not be able to take action promptly, increasing the risk of successful fraudulent account takeovers. |
Addressing these weaknesses is crucial for DeBank to enhance the security of its account recovery process. By implementing stronger identity verification methods, improving the password reset mechanism, offering additional verification options, and implementing robust monitoring and notification systems, DeBank can better protect its customers’ accounts and prevent unauthorized access.
Analyzing DeBank’s Transaction Monitoring System
DeBank’s transaction monitoring system plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of its digital banking platform. By carefully analyzing and monitoring each transaction, DeBank can detect any suspicious activities or potential fraud attempts. This system employs advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify patterns and anomalies in transactions, allowing DeBank to take prompt action when necessary.
One of the key features of DeBank’s transaction monitoring system is its real-time monitoring capability. This enables DeBank to track transactions as they are happening, allowing for immediate detection of any suspicious activities. By constantly scanning for unusual patterns or large transactions, DeBank can quickly identify potential risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
The transaction monitoring system also utilizes various parameters and rules to evaluate transactions. These parameters can include transaction amount, frequency, geographic location, and user behavior. By applying these parameters and rules, DeBank can identify transactions that deviate from the norm and raise a red flag for further investigation.
In addition, DeBank’s transaction monitoring system incorporates data from external sources to enhance its accuracy and effectiveness. By comparing transaction details with information from financial institutions, credit bureaus, and law enforcement agencies, DeBank can identify potential money laundering activities or fraudulent transactions. This integration of external data helps DeBank stay one step ahead in detecting and preventing financial crimes.
To ensure the integrity of its transaction monitoring system, DeBank maintains a team of experienced analysts who are responsible for reviewing flagged transactions and conducting investigations when necessary. These analysts work in close collaboration with other departments within DeBank to gather additional information and make informed decisions regarding suspicious activities.
Overall, DeBank’s transaction monitoring system is a robust and proactive tool that helps safeguard its digital banking platform from various threats. By leveraging advanced technology, real-time monitoring, and external data sources, DeBank can effectively detect and prevent fraudulent activities, ensuring the security and trust of its customers.
The Threat of Malware in DeBank’s Online Banking
One of the key vulnerabilities in DeBank’s online banking system is the threat of malware. Malware, short for malicious software, is designed to infiltrate computer systems, steal sensitive information such as login credentials, and gain unauthorized access to personal and financial data.
Malware can be delivered through various means, including infected email attachments, malicious websites, and compromised software downloads. Once installed, it can run silently in the background, collecting data and transmitting it to remote servers controlled by cybercriminals.
Types of Malware
There are several types of malware that pose a threat to DeBank’s online banking system:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Trojan Horse | A type of malware that disguises itself as a legitimate application or file. It often tricks users into installing it by posing as a useful program. |
| 2. Keylogger | A program that records keystrokes on a computer, allowing cybercriminals to capture sensitive information such as passwords and credit card numbers. |
| 3. Banking Trojan | A specialized type of Trojan horse that specifically targets online banking transactions. It can intercept user inputs, redirect online payments, and modify account balances. |
| 4. Ransomware | A type of malware that encrypts a user’s files or locks their computer, demanding a ransom payment in exchange for restoring access. |
Impact on Online Banking
The presence of malware in DeBank’s online banking system can have severe consequences:
- Loss of sensitive customer data, including usernames, passwords, and financial information.
- Identity theft, where cybercriminals use stolen information to impersonate customers and conduct fraudulent activities.
- Unauthorized transactions and fund transfers, leading to financial loss for both DeBank and its customers.
- Damage to DeBank’s reputation, as customers may lose trust in the security of the online banking system.
To mitigate the threat of malware, DeBank should implement robust security measures, such as regularly updating antivirus software, conducting regular security audits, and educating customers about safe online banking practices.
Evaluating DeBank’s Response to Data Breaches
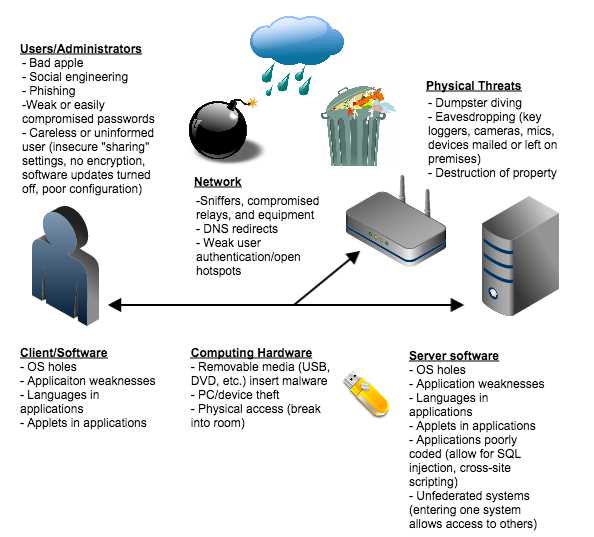
Data breaches are a major concern in the digital banking industry, as they can expose sensitive customer information and undermine trust in financial institutions. It is essential for banks like DeBank to have a robust and effective response plan in place to address data breaches swiftly and effectively.
Timely Detection and Notification
One crucial aspect of evaluating DeBank’s response to data breaches is the speed at which they are able to detect and identify a breach. By investing in state-of-the-art security systems and employing skilled cybersecurity professionals, DeBank can enhance their ability to detect breaches early on. This is critical because the sooner a breach is detected, the sooner appropriate measures can be taken to mitigate its impact. Additionally, DeBank should have a well-defined process for notifying affected customers promptly and transparently, providing them with clear instructions on how to protect their accounts and personal information.
Effective Incident Response and Remediation
DeBank’s response to data breaches should also include a well-prepared incident response plan. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including containment, investigation, and remediation. DeBank should have a team of experienced professionals who are trained to handle such incidents and who can work quickly to limit the damage and prevent further unauthorized access. This could involve isolating affected systems, patching vulnerabilities, and conducting thorough forensic analysis to determine the scope of the breach.
Moreover, DeBank should also consider providing affected customers with additional security measures, such as credit monitoring services or password resets, to mitigate the risk of identity theft or fraudulent activity.
Regular Testing and Improvement
Finally, to effectively evaluate DeBank’s response to data breaches, it is important to consider their commitment to regular testing and improvement of their incident response plan. By conducting simulated breach exercises and incorporating lessons learned into their response protocols, DeBank can continuously enhance their ability to respond effectively to future incidents. Regular evaluation and enhancement of security measures and protocols are crucial in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
In conclusion, evaluating DeBank’s response to data breaches involves assessing their ability to detect breaches in a timely manner, promptly notify affected customers, execute an effective incident response plan, and continuously improve their response capabilities. By excelling in these aspects, DeBank can demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer data and maintaining a high level of trust and security in their digital banking services.
Strengthening DeBank’s Cybersecurity Measures
As the digital banking industry continues to grow rapidly, it is crucial for DeBank to prioritize and enhance its cybersecurity measures. Ensuring the security and privacy of customer data is of utmost importance in building trust and protecting against potential threats. Here are some key steps that DeBank can take to strengthen its cybersecurity measures:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) |
| 2 | Regularly Update and Patch Software |
| 3 | Enable Encryption for Data Transmission |
| 4 | Train Employees on Cybersecurity Best Practices |
| 5 | Implement a Robust Firewall |
| 6 | Establish Incident Response and Recovery Plans |
| 7 | Regularly Conduct Security Audits |
By implementing multi-factor authentication, DeBank can add an extra layer of security to the login process, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to customer accounts. Regularly updating and patching software is crucial in order to fix any vulnerabilities or bugs that may be exploited by attackers.
Enabling encryption for data transmission ensures that sensitive customer information is protected while being transmitted over networks. Additionally, training employees on cybersecurity best practices can help prevent social engineering attacks and ensure that they are aware of potential threats.
A robust firewall is essential for monitoring and filtering network traffic, preventing unauthorized access and protecting against various types of cyber threats. Establishing incident response and recovery plans allows DeBank to effectively respond to and mitigate the impact of any security incidents that may occur.
Regular security audits are necessary to assess the effectiveness of DeBank’s cybersecurity measures and identify any potential weaknesses or areas for improvement. By consistently evaluating and strengthening its cybersecurity measures, DeBank can better protect its customers’ sensitive data and maintain trust in the digital banking industry.
FAQ:,
What are the common weak points in digital banking?
Common weak points in digital banking include vulnerability to cyberattacks, insufficient encryption measures, weak authentication methods, and the potential for data breaches.
How can cyberattacks target digital banking platforms?
Cyberattacks can target digital banking platforms through various means, such as malware injections, phishing scams, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and social engineering techniques.
What are the consequences of a data breach in digital banking?
The consequences of a data breach in digital banking can be severe, including unauthorized access to sensitive customer information, financial losses, damaged reputation for the bank, and potential legal and regulatory consequences.